Setting up a TP-Link router is a straightforward process that can significantly enhance your home network experience. Whether it’s to support a fleet of devices or to ensure steady internet connectivity, mastery of your router’s configuration is key. This guide will equip users with a step-by-step approach to installing and configuring their TP-Link routers efficiently. TP-Link’s user-friendly interface and the simplicity of its setup procedures mean that even users with minimal technical background can secure and manage their home networks with ease.
Understanding how to configure a TP-Link router not only ensures a stable internet connection but also helps in optimizing the network’s performance. Users will learn how to access the router’s settings, create a secure wireless network, and adjust various features to suit their specific internet needs. Personalizing Wi-Fi names, setting up guest networks, and securing the router with a unique password are among the initial steps users will be guided through.
With security becoming an ever-increasing concern, this guide also offers insights into advanced features such as parental controls and firmware updates. Configuring these settings bolsters network security and helps to protect against potential cyber threats. Moreover, users will discover how to troubleshoot common issues, ensuring they can maintain a reliable and secure network environment. This knowledge not only enhances the user’s ability to manage their home network but also empowers them to make informed decisions about their network settings in the future.
Understanding Your TP-Link Router
To effectively set up and utilize a TP-Link router, one should be acquainted with its features, hardware components, and the variations among different models.
Features and Capabilities
TP-Link routers offer a range of attributes that enhance the user’s internet experience. Key features typically include:
- Dual-band or tri-band frequencies: Offering 2.4GHz and 5GHz bands for a balance between range and performance, with select models providing a third band to minimize congestion.
- MU-MIMO technology: Allows multiple devices to receive data simultaneously, improving efficiency in device-heavy networks.
- Parental controls and guest networks: Enables users to manage internet access and create separate networks for visitors.
- Advanced security: WPA/WPA2 encryption and firewall protections keep the network secure from external threats.
Hardware Overview
The physical components of a TP-Link router are integral to its operation. Some crucial aspects include:
- Ports: Routers come with varying numbers of Ethernet ports for wired connections and a WAN port for the internet connection.
- Antennas: The number and type of antennas affect coverage and signal strength; some are internal while others are external and adjustable.
- Processor and RAM: The processor’s speed and the amount of RAM contribute to the router’s overall performance and ability to handle multiple devices.
Model Comparison
Different models cater to various needs and environments. A simple comparison table helps in identifying the right model:
| Model | Frequency Bands | Antennas | Ethernet Ports | MU-MIMO | Processor Speed | RAM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Archer C60 | Dual-band | 5 (Fixed) | 4x LAN, 1x WAN | No | 900 MHz | 64 MB |
| Archer A7 | Dual-band | 3 (External) | 4x LAN, 1x WAN | Yes | 750 MHz | 128 MB |
| Archer C4000 | Tri-band | 6 (External) | 4x LAN, 1x WAN | Yes | 1.8 GHz | 512 MB |
| Archer AX6000 | Dual-band | 8 (External) | 8x LAN, 1x WAN | Yes | 1.8 GHz | 1 GB |
| Archer AX50 | Dual-band | 4 (External) | 4x LAN, 1x WAN | Yes | 1.5 GHz | 256 MB |
| Archer C1200 | Dual-band | 3 (Fixed) | 4x LAN, 1x WAN | No | 1 GHz | 128 MB |
| Archer C9 | Dual-band | 3 (External) | 4x LAN, 1x WAN | No | 1 GHz | 128 MB |
| Archer AX10 | Dual-band | 4 (Fixed) | 4x LAN, 1x WAN | Yes | 1.5 GHz | 256 MB |
The table enables quick assessment of essential features, aiding the selection of a router that fits the user’s needs.
Preparation for Installation
Before starting your TP-Link router setup, ensuring you have everything needed for a smooth installation is crucial. This means verifying the contents of your package, determining the ideal location for your router, and having the necessary tools and information at hand.
Checking Package Contents
- Router: Confirm the presence of the TP-Link router itself.
- Power adapter: Ensure the correct adapter for your model is included.
- Ethernet cable: Look for at least one Ethernet cable for initial configuration.
- Quick Installation Guide: This should detail the setup process.
- Wi-Fi Info Card: Provides default wireless network details.
Positioning Your Router
- Central Location: Place your router centrally to distribute Wi-Fi evenly.
- Elevated Position: Keep it off the floor, ideally on a shelf or desk.
- Away from Obstructions: Avoid physical obstructions like walls and metal objects.
- Distance from Electronics: Separate it from other electronic devices that could cause interference.
Required Tools and Information
- Computer or Mobile Device: You will need one to access the router’s web interface.
- Internet Connection Details: Have your internet service provider (ISP) credentials ready if needed.
- Browser: Ensure you have a web browser installed on your device for accessing the router setup page.
Connecting Your Router
The initial setup of a router involves establishing the physical connections, powering the device, and navigating the initial boot process. These are essential steps to ensure that the router functions properly and can connect to the internet.
Physical Connection Setup
For proper routing functionality, one must connect the TP-Link Router to their modem or primary gateway. Follow these steps:
- Locate the Ethernet port on the back of the router labeled either “Internet” or “WAN.”
- Use an Ethernet cable to connect this port to the modem’s Ethernet port.
- Connect any devices that require a wired connection to the available LAN ports using additional Ethernet cables.
Powering On the Router
To begin using the router, it must be powered correctly:
- Plug in the router’s power adapter to an appropriate electrical outlet.
- Press the power button on the router if it has one, or the device will power on automatically when plugged in.
Initial Boot Process
After the router is powered on, the following will occur:
- The lights on the router will indicate that it’s being powered. A blinking power light typically shows the booting process.
- Wait for the power light to become steady, indicating the router has completed the initial boot and is ready for configuration.
Configuring Basic Settings
In configuring a TP-Link router, one must first access the router’s web interface, set a personalized network name and password, establish the internet connection, and ensure the device’s firmware is up-to-date for optimal security and performance.
Step-by-Step TP-Link Router Setup Guide:
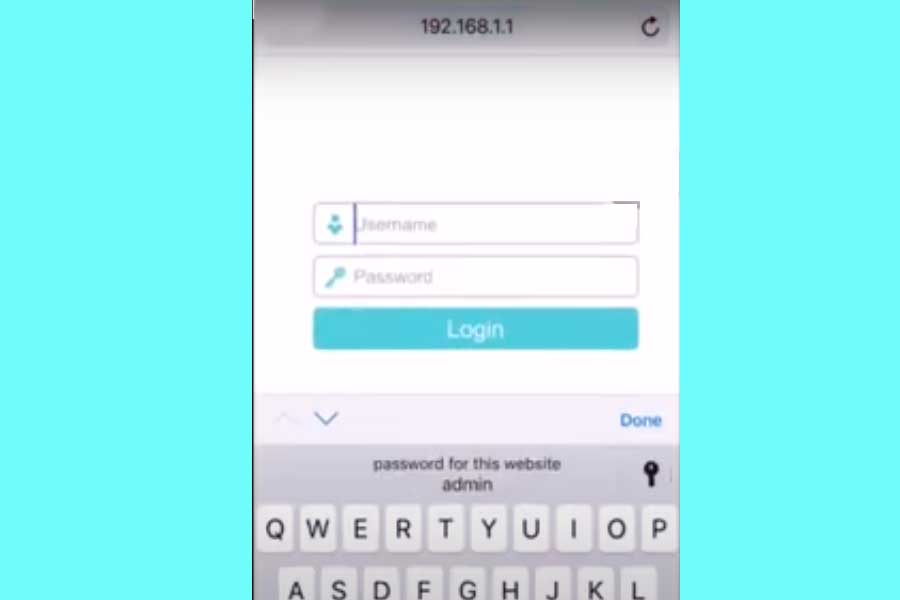
Accessing the Web-Based Setup Page
To access the TP-Link router’s setup page, connect the router to a computer using an Ethernet cable or Wi-Fi. Open a web browser and enter http://192.168.0.1 or http://192.168.1.1 in the address bar. When prompted, enter the default username and password, typically admin for both.
Creating a Network Name and Password
Create a unique SSID (Service Set Identifier) for your wireless network under the Wireless settings. Ensure the SSID is identifiable and not easily guessed. Set a strong password by navigating to Wireless Security and selecting WPA/WPA2-Personal. Choose a password that is a combination of letters, numbers, and special characters.
Setting Up Internet Connection
Under the Network settings, select WAN (Wide Area Network) to configure your internet connection. Choose the correct connection type provided by your ISP (Internet Service Provider)—such as Dynamic IP, Static IP, or PPPoE. Input the necessary information such as username and password for PPPoE, or IP address for a Static IP, then save the settings.
Updating Router Firmware
Regular firmware updates are crucial for security and performance. Check for updates by going to the System Tools and selecting Firmware Upgrade. If available, download and install the latest firmware version following the on-screen instructions. Avoid interrupting the process to prevent router malfunctions.
Advanced Configuration
This segment provides an in-depth look into securing your network, setting up guest access, implementing parental restrictions, and managing bandwidth priority through Quality of Service (QoS) settings.
Network Security Settings
To enhance your network’s security, change the default administrator password. Navigate to System Tools and select Change Password. For added protection, adjust the encryption settings under Wireless Settings to WPA2-PSK with AES encryption.
- Change default admin password
- Set encryption to WPA2-PSK with AES
Guest Network Setup
Establish a guest network to ensure the main network remains secure. In the router settings, go to Guest Network, enable the network, and create a unique SSID and password. Ensure guest access is isolated from the main network.
- Enable Guest Network
- Set SSID and password
- Isolate from main network
Parental Controls
Parental controls restrict internet access to maintain a child-friendly online environment. Access Parental Controls in the menu, enable the feature, and specify the devices and URLs to be restricted. Schedule access times for added control.
- Enable Parental Controls
- Specify devices and URLs
- Set internet access schedules
Managing QoS
Quality of Service (QoS) prioritizes traffic to ensure stable performance for high-priority tasks. Go to Bandwidth Control, enable QoS, and create rules to prioritize devices or applications that require stable connections, such as video conferencing or online gaming.
- Enable QoS in Bandwidth Control
- Prioritize devices or applications
Connecting Devices
To connect devices to your TP-Link router, one should follow these methodical steps:
- Wireless Connection:
- Ensure the router is powered on and the LED indicators are stable.
- On the device (laptop, smartphone, etc.), navigate to the Wi-Fi settings.
- Search for the network name (SSID) associated with your TP-Link router—it may be on the bottom label.
- Select the SSID and enter the default wireless password, typically found on the router or in the documentation.
- Wired Connection:
- Use an Ethernet cable to connect the device directly to the router.
- Insert one end of the cable into the device’s Ethernet port.
- Insert the other end into one of the router’s LAN ports (not the WAN port).
- WPS Setup:
- Some devices support Wi-Fi Protected Setup (WPS).
- Press the WPS button on your TP-Link router.
- Within two minutes, activate the WPS function on the device you want to connect.
Connection Tips:
- Use a strong password to enhance security after the initial setup.
- For optimal performance, place your router central to the devices connecting to it.
- Limit obstructions such as walls or large electronic appliances between the devices and router for better signal strength.
- It is recommended to update the firmware post-setup to the latest version for enhanced features and security.
Remember to save the configuration changes on your router after connecting your devices.
Troubleshooting
When configuring a TP-Link router, the user may encounter issues. The troubleshooting process is essential to resolve these problems efficiently. Here are common issues and steps to troubleshoot them.
Cannot Access the Router’s Web Interface:
- Verify the router is correctly powered on.
- Ensure the device is connected to the TP-Link network.
- Confirm the correct IP address, typically
192.168.0.1or192.168.1.1. - Clear the browser cache or try a different browser.
Internet Connection is Unstable or Slow:
- Check Cables: Ensure all cables are securely connected.
- Restart: Power cycle the router and modem.
- Interference: Move the router away from interference sources (e.g., microwaves, cordless phones).
- Channel: In the router settings, switch to a less crowded Wi-Fi channel.
Router Login Credentials Not Working:
- Confirm the default credentials (
adminfor both username and password); refer to the router’s manual if changed. - If credentials were changed and forgotten, a factory reset may be necessary. Use a paperclip to press and hold the reset button for 10 seconds.
| Issue | Possible Cause | Step to Fix |
|---|---|---|
| Connectivity | Faulty cable or port | Replace or reconnect cables |
| Slow Speed | Overcrowded network channel | Change Wi-Fi channel |
| Access Error | Incorrect IP or browser cache issue | Verify IP/check browser |
| Forgotten Credentials | Changed and not recorded credentials | Reset to factory settings |
For further issues that cannot be resolved through these steps, the TP-Link support page or contacting customer support is recommended.
Maintenance and Management
Regular maintenance and effective management are crucial for ensuring that a TP-Link router performs optimally. It involves periodic updates, secure password management, and network health checks.
Firmware Updates:
- Ensure the router’s firmware is updated to the latest version.
- Check for updates manually through the TP-Link admin panel or enable automatic updates.
Password Management:
- Change default passwords to avoid unauthorized access.
- Use a combination of letters, numbers, and symbols for strong passwords.
Network Checks:
- Monitor connected devices: Regularly check on the devices connected to your network.
- Speed tests: Conduct speed tests to ensure the network is functioning at the desired speed.
Backup Settings:
- It is critical to back up the current settings of the router.
- Use the TP-Link admin interface to save a configuration file.
Restart Schedule:
- Setting a schedule to regularly reboot the router can prevent performance issues.
- Rebooting can be done manually or automatically if supported by the TP-Link model.
| Activity | Interval | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Firmware Updates | As released | Keeps router secure |
| Password Changes | Every 3-6 months | Enhances security |
| Network Checks | Bi-weekly | Ensures stable performance |
| Backup Settings | After any change | Allows quick restoration |
| Router Reboots | Monthly | Maintains router health |
Proper maintenance and management help to maintain optimal performance, enhance security, and extend the lifespan of a TP-Link router.
Additional Features
Most TP-Link routers come with a range of additional features that enhance network performance and security. Users can benefit from these to manage their home network more effectively.
Guest Network: This feature allows for the creation of a separate network for guests. It grants internet access while keeping your main network secure.
Parental Controls: Provides the ability to restrict access to inappropriate content and set time limits on internet usage.
QoS (Quality of Service): Prioritizes traffic to ensure better performance for critical devices and applications, such as gaming consoles or streaming services.
Bandwidth Control: Limits the amount of bandwidth available to individual devices to prevent any one device from consuming all the network resources.
VPN Server/Client: With VPN support, users can securely access their home network remotely.
IPv6 Support: Future-proofs the network by providing support for the latest internet protocol version, IPv6.
The following table summarizes these features for easy reference:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Guest Network | Separate access for guests, isolates from main network. |
| Parental Controls | Manage content and access times for network users. |
| QoS | Allocate network priority to specific devices or activities. |
| Bandwidth Control | Limit individual device bandwidth usage. |
| VPN Support | Securely access network from different locations. |
| IPv6 Support | Ensures compatibility with new Internet Protocol Version. |
To configure these features, users typically need to access the router’s web interface using its IP address or through the TP-Link Tether app. It is important to review the router’s manual for specific directions on enabling and customizing these functions to meet individual needs.
Support and Warranty Information
TP-Link routers come with a limited warranty from the date of purchase. Consumers should register their product immediately after purchase to benefit from the company’s warranties and access support more efficiently.
Coverage:
- The warranty typically covers manufacturing defects.
- It usually does not cover damages caused by accidents or unauthorized modifications.
Duration:
- Warranty periods can vary by product.
- Generally, TP-Link offers a 2-year warranty for most routers.
Support:
| Channels | Description |
|---|---|
| Website | Access FAQs, firmware updates, and troubleshooting guides. |
| Support App | Use the TP-Link Tether app for guided assistance. |
| Hotline | Call the TP-Link hotline for direct support during business hours. |
| Email TP-Link’s support for a detailed inquiry and receive a response within a few business days. | |
| Community | Engage with other TP-Link users in forums to share information and solutions. |
Before contacting support, one should have the model number and purchase details at hand. TP-Link’s official website provides more comprehensive information regarding possible extended warranties or local variations in warranty terms. Remember, preserving the receipt and complying with the warranty’s terms are vital for a smooth support experience.